Flow Measurement

Overview
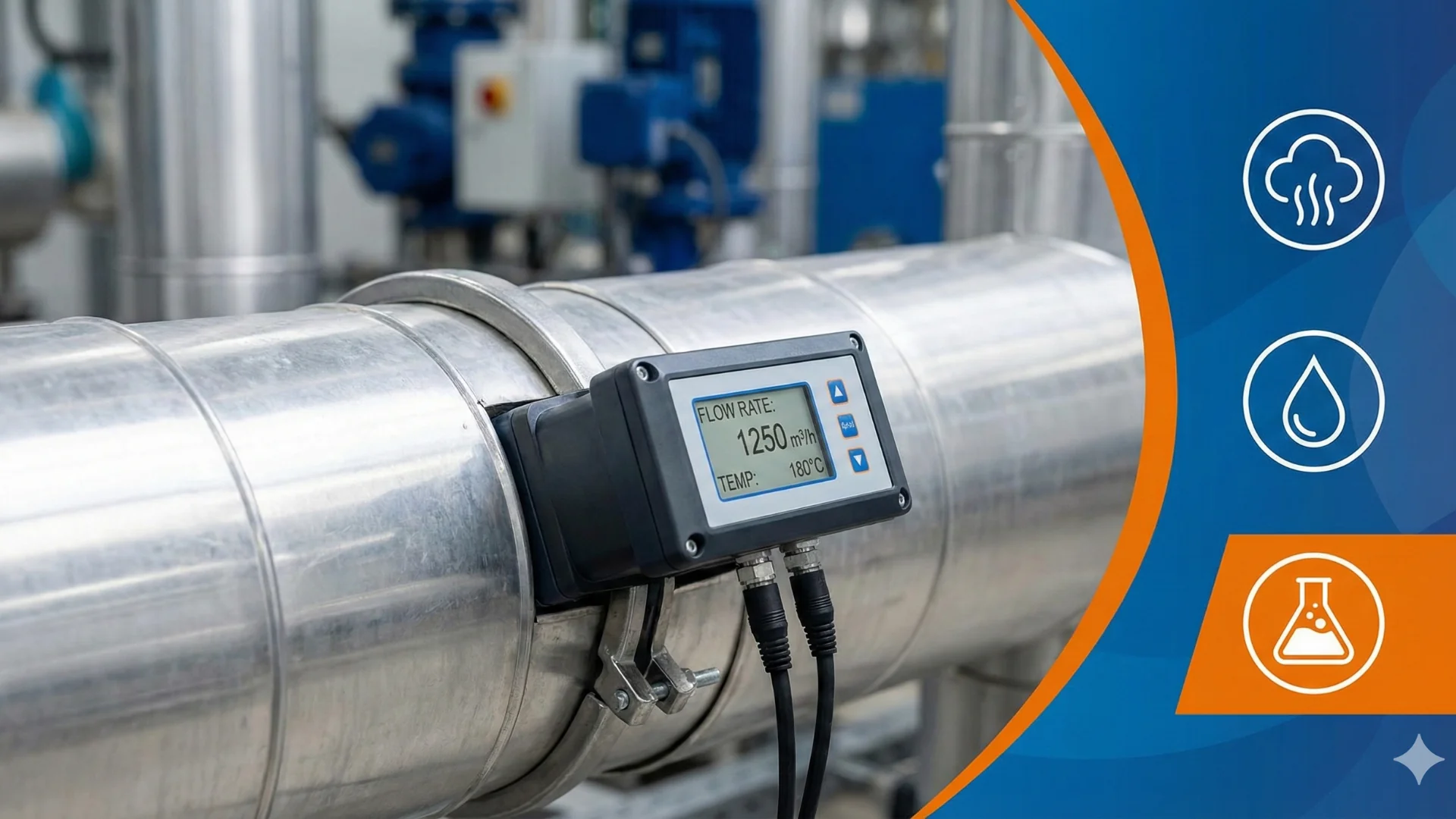
Accurate flow measurements are critical to the calculation of Utility or process control applications. Flow Measurement is also useful for monitoring & troubleshooting internal processes at various points. measures the flow of virtually any fluid, be it liquid, gas or steam, regardless of the flow direction (bi-directional) and over an extremely wide measuring range. Due to its practical advantages, external flow measurement with clamp-on ultrasonic transducers has become a standard measuring technique in a broad range of industries and applications. This flowmeter can be installed in just minutes without needing to shut down, thus avoiding costly downtime. This ultrasonic technology works with gases at high or low pressure in pipes made of metal and most other materials.
Principle
In general, ultrasonic flow meters work by transmitting ultrasonic waves and tracking how long it takes that sound to return to the unit. Clamp-on ultrasonic systems determine the volumetric flow rate according to the transit-time difference method. Since the ultrasonic signal that is irradiated into the pipe is carried by the fluid flowing inside, a time delay occurs between the acoustic transit time both with and against the flow of direction. This time delay can be measured very accurately. The transmitter calculates the volumetric flow rate based on the parameters input for the pipe geometry and the physical properties of the fluid stored in the internal database.
Type of Flow Measuring Service Provide
Steam Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: Flow measurement of saturated steam up to max. 180 °C
- Pipe Size: 30mm to 360 mm
Thermic Fluid Heater Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 240 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 1000 mm
Boiler Feed Water Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 240 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 1000 mm
Process Condensate Water Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 240 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 1000 mm
Brine chiller Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to -30 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm
Fire Fighting Line Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm
ETP Line Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm.
Water Pumping Station Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm.
Borewell Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm.
Chemical Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm.
Process Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm.
Cooling Tower Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm.
Condenser Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm.
Chiller Flow Measurement
- Temperature Range: up to 130 °C
- Pipe Size: 15mm to 6500 mm.
Features
Applications
Explore Related Services
View All Services →
Energy Audit is defined as “the verification, monitoring and analysis of use of energy including submission of technical report containing recommendations for improving energy efficiency with cost benefit analysis and an action plan to reduce energy consumption”. It builds on the principle "you can't manage what you don't measure". It essentially combines the principles of energy use and statistics.

Energy conservation is the effort made to reduce the consumption of energy by using less of an energy service. This can be achieved either by using energy more efficiently (using less energy for a constant service) or by reducing the amount of service used (for example, by driving less).

Harmonic analysis is a technique used to study and analyze the harmonic components in a periodic waveform or signal. The main use of harmonic analysis in electrical engineering is to examine the existence and properties of harmonics in electrical power systems. Harmonic voltage or current waveform frequencies are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency. However, due to non-linear loads, such as power electronics, variable speed drives, and certain types of lighting, harmonic currents and voltages can be introduced into the system.

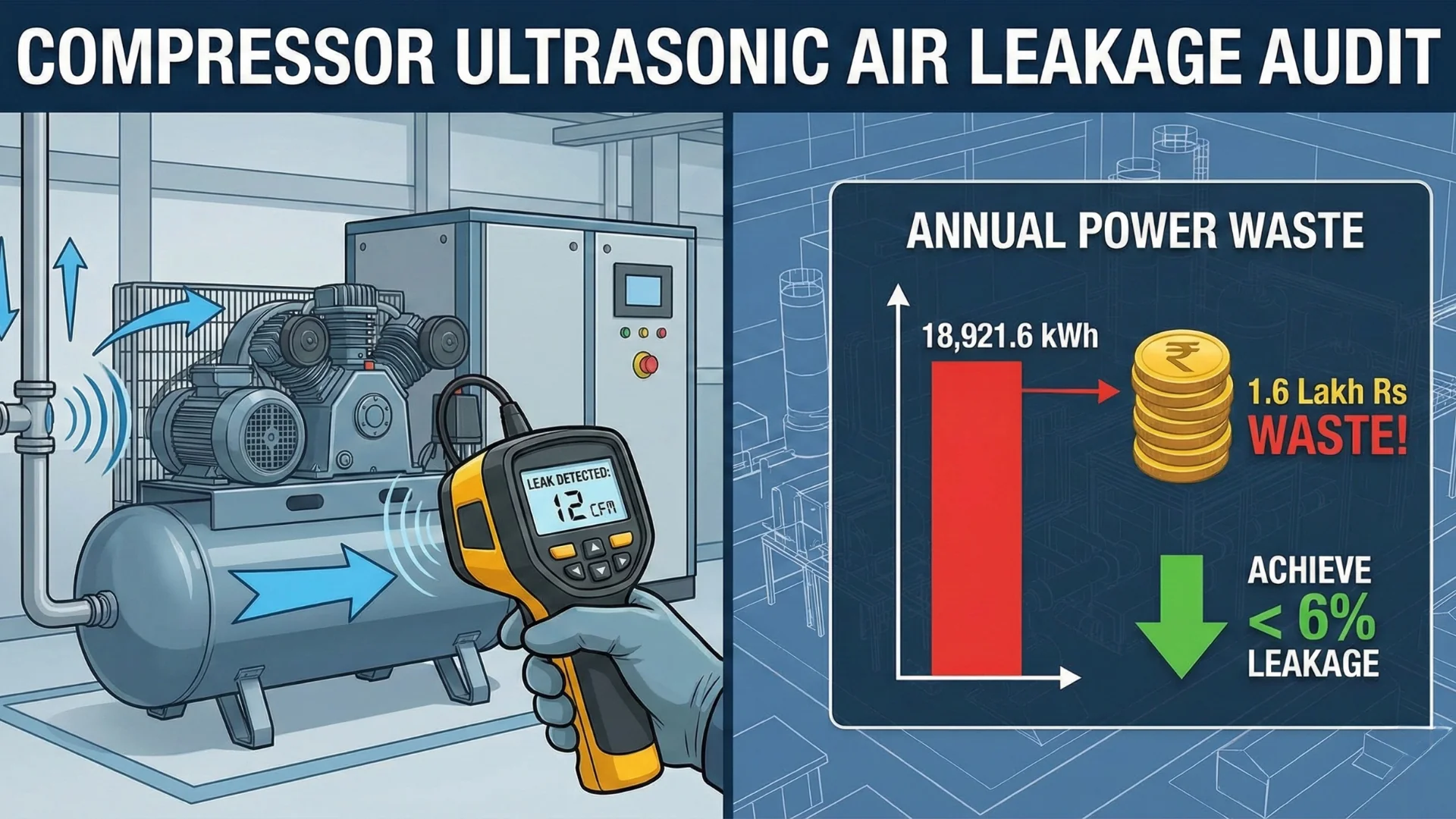
A compressed air audit effectively identifies inefficiencies, reduces energy costs, and improves system performance. Many industrial air compressors operate inefficiently due to leaks, artificial demand, and incorrect air pressure requirements, unnecessarily increasing cost per kWh.