Electrical Motor Efficiency Study

Overview
The motor efficiency can be calculated from the total losses, which are assumed to be the summation of the following losses.
Losses considered:
The stray losses are difficult to measure with any accuracy. IEEE Standard 112 gives a complicated method. Which is rarely used on shop floor. IS & IEC standards take fixed value as 0.5% of output. It must be remarked that actual value of stray losses is likely to be more. IEEE – 112 specifies values from 0.9 to 1.8%.
Case Study
Overview
- Application: All Induction motor more than 50HP.
- Type of Audit: Motor Efficiency Study.
Motor Efficiency Calculation
| SN | Descriptions | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No of poles | - | 6 |
| 2 | Winding connection | - | DELTA |
| 3 | Type | - | TEFC |
| 4 | Output | kW | 180 |
| 5 | Voltage | Volts | 415 |
| 6 | Full load current, Ifl | Amp | 311 |
| 7 | Phase current at Full load, Ifl-ph | Amp | 179.6 |
| 8 | Speed | rpm | 990 |
| 9 | Frequency | Hz | 50 |
| 10 | Full load slip | p.u. | 0.010 |
| 11 | Efficiency | % | 90 |
| 12 | Insulation | - | Class F |
| 13 | Full load winding temperature | 0C | 85 |
| -- | No load test | -- | -- |
| 14 | Line voltage, U | Volts | 415.67 |
| 15 | Line Current, Inl | Amp | 118.7 |
| 16 | Phase current, Inl-ph | Amp | 68.5 |
| 17 | No load power input, Pi-nl | Watts | 9183 |
| 18 | Stator phase resistance at cold condition | Ohms | 0.4333 |
| 19 | Stator phase resistance after no load test | Ohms | 0.4333 |
| 20 | Ambient Temperature, Ta | 0C | 30 |
| 21 | Frequency, f | Hz | 50 |
| 22 | Winding resistance at full load Rph-fl | Ohms | 0.5233 |
| -- | Calculation of losses | -- | -- |
| 23 | No load power input, Pi-nl | Watts | 9183.33 |
| 24 | No load stator copper loss at T1 Temp. | Watts | 6102.1 |
| 25 | Iron, friction and windage loss | Watts | 3081.23 |
| 26 | Stator full load copper loss | Watts | 50611.24 |
| 27 | Synchronous speed | - | 1000.0 |
| 28 | Full load slip | - | 0.01 |
| 29 | Rotor Input power | kW | 181.82 |
| 30 | Rotor ohomic loss | kW | 1.8 |
| 31 | Stray loss 1.5% | kW | 2.7 |
| 32 | Total loss | kW | 58.21 |
| 33 | Motor full load input power | kW | 238.2 |
| 34 | Efficiency | % | 75.563 |
Explore Related Services
View All Services →
Energy Audit is defined as “the verification, monitoring and analysis of use of energy including submission of technical report containing recommendations for improving energy efficiency with cost benefit analysis and an action plan to reduce energy consumption”. It builds on the principle "you can't manage what you don't measure". It essentially combines the principles of energy use and statistics.

Energy conservation is the effort made to reduce the consumption of energy by using less of an energy service. This can be achieved either by using energy more efficiently (using less energy for a constant service) or by reducing the amount of service used (for example, by driving less).

Harmonic analysis is a technique used to study and analyze the harmonic components in a periodic waveform or signal. The main use of harmonic analysis in electrical engineering is to examine the existence and properties of harmonics in electrical power systems. Harmonic voltage or current waveform frequencies are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency. However, due to non-linear loads, such as power electronics, variable speed drives, and certain types of lighting, harmonic currents and voltages can be introduced into the system.

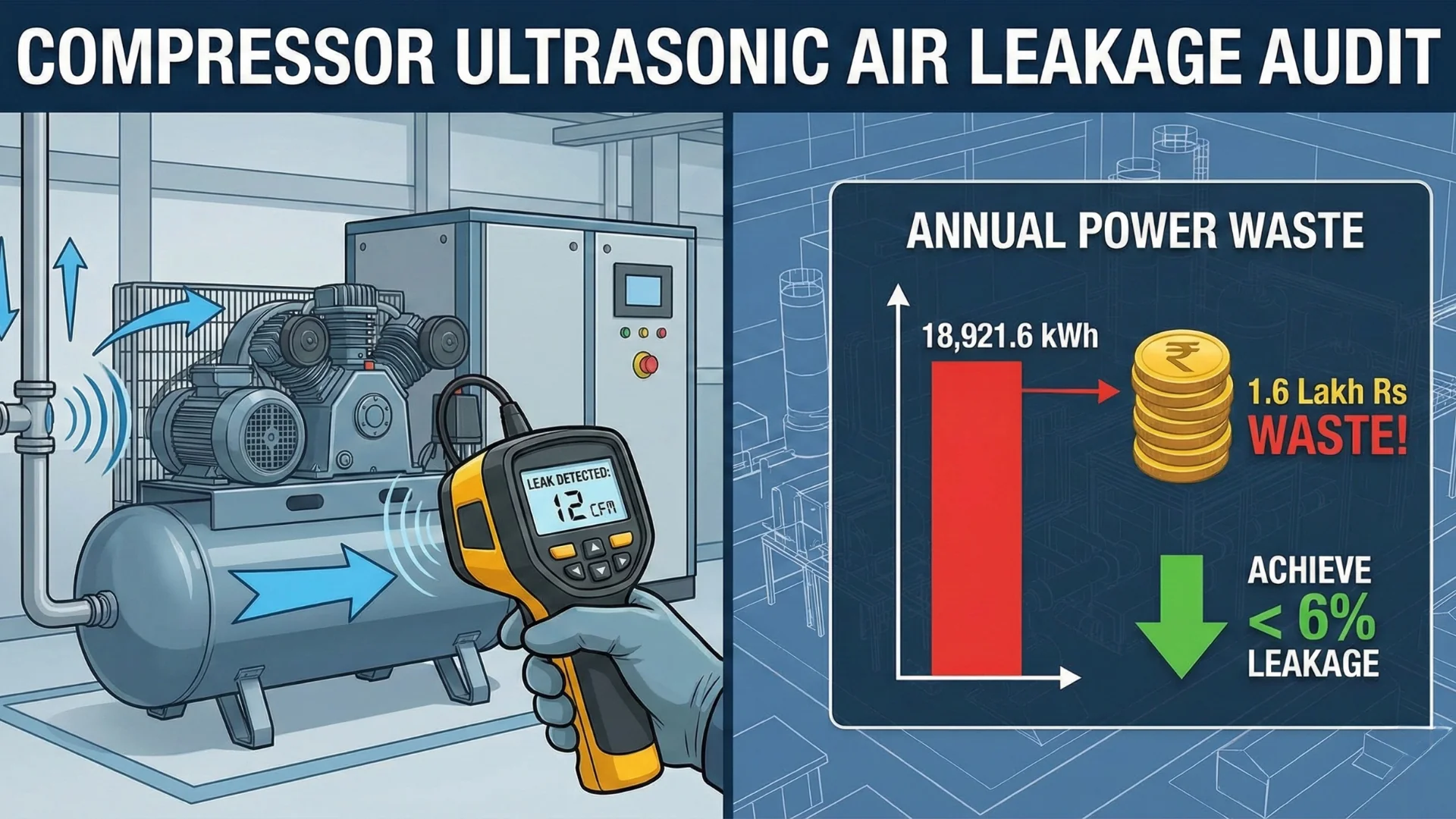
A compressed air audit effectively identifies inefficiencies, reduces energy costs, and improves system performance. Many industrial air compressors operate inefficiently due to leaks, artificial demand, and incorrect air pressure requirements, unnecessarily increasing cost per kWh.