Process Heat Mass Balance

Overview
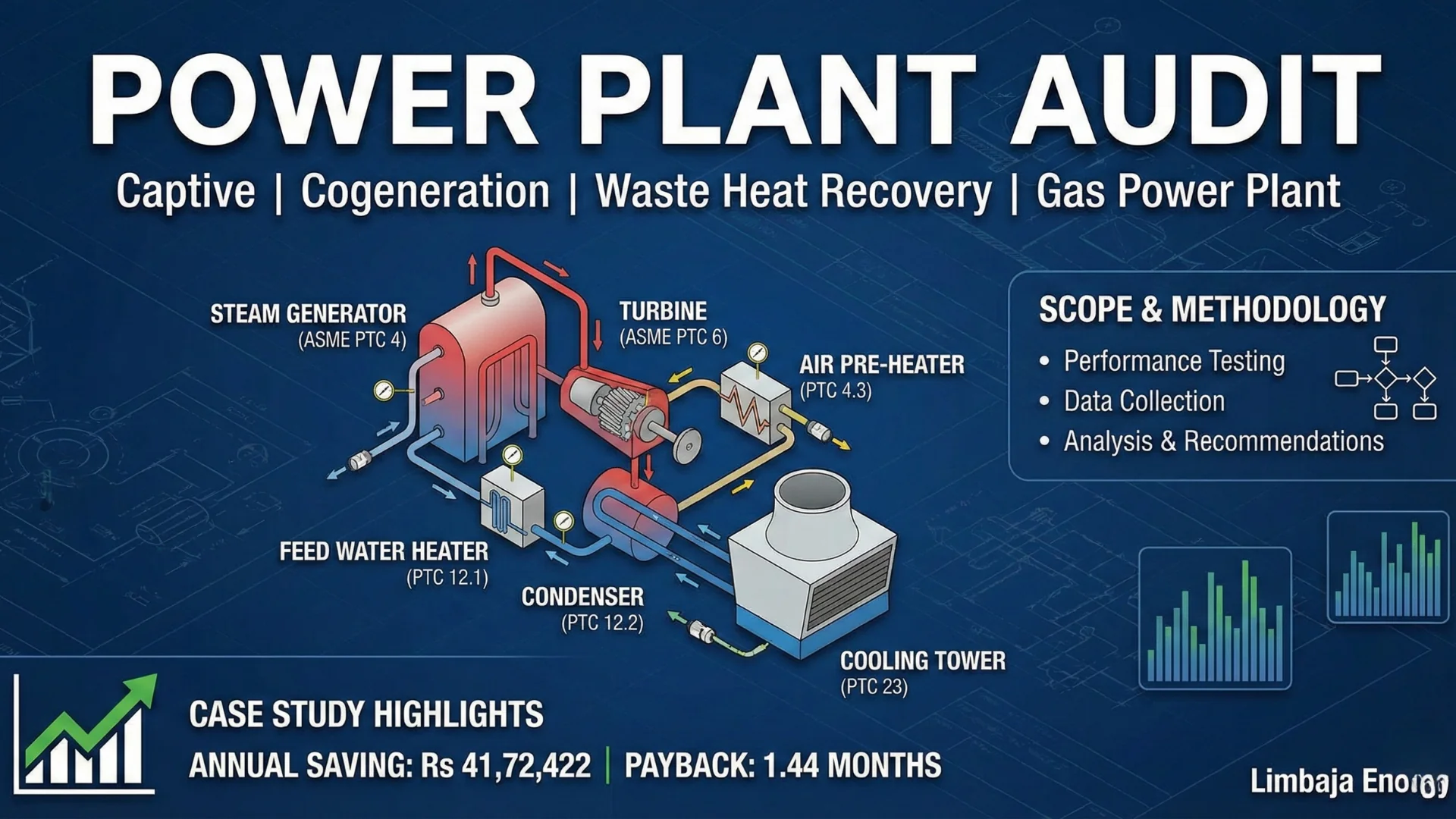
Heat and mass balance is a critical aspect of process engineering, used extensively in the design and analysis of process plants. These calculations ensure that the energy and material inputs and outputs in a system are accurately accounted for, helping to optimise efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness in industrial operations.
Key Components
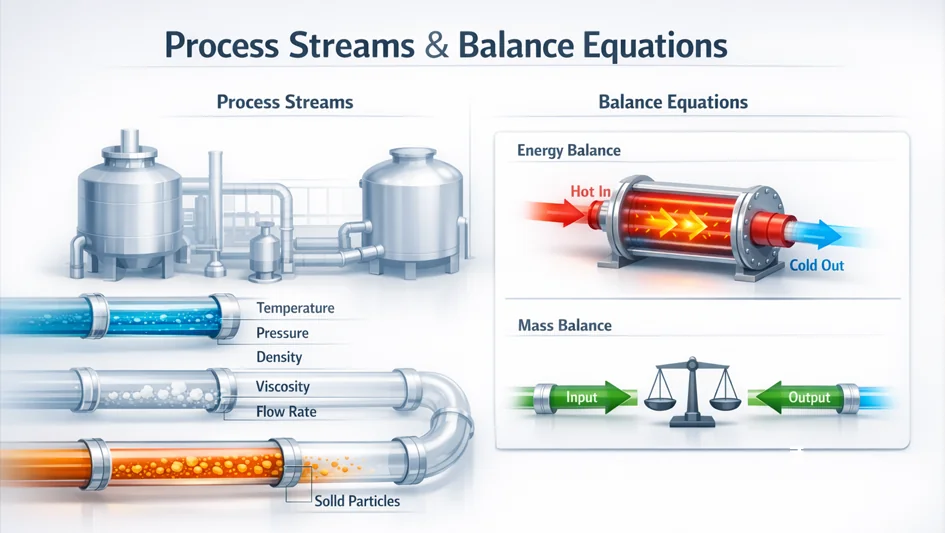
Key Components
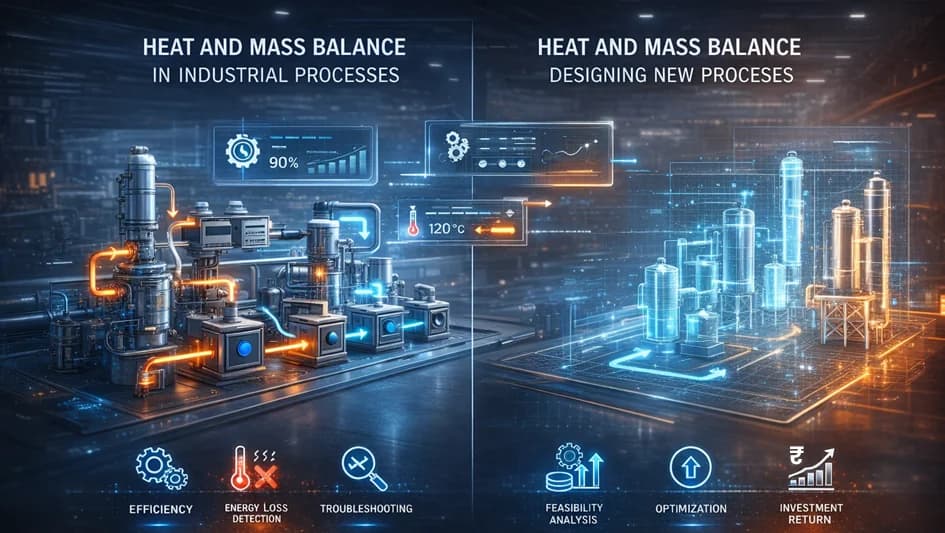
Heat and Mass Balance in Existing Processes
In existing industrial processes, heat and mass balance calculations are essential for optimising operational efficiency and troubleshooting. These calculations help identify inefficiencies, energy losses, and areas for improvement. Regular evaluations ensure safety and reliability by detecting deviations from expected performance, allowing for timely maintenance and adjustments.
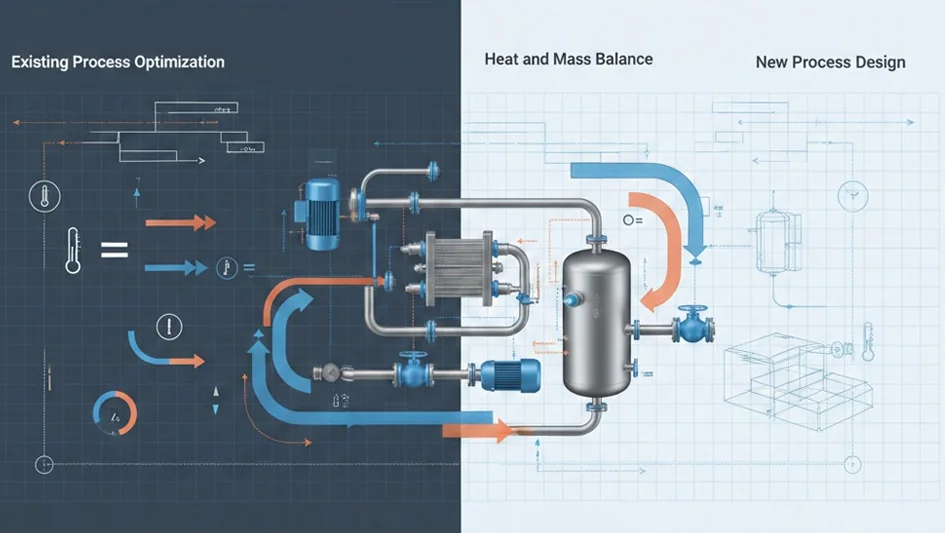
Heat and Mass Balance in New Processes
For new processes, heat and mass balance calculations are fundamental during the development phase. They provide insights into expected material and energy flows, guiding the design of equipment and selection of materials. These analyses are crucial for feasibility studies, enabling engineers to evaluate different configurations and technologies to identify the most cost-effective and efficient solutions.
By applying heat and mass balance principles, engineers can ensure processes are both efficient and cost-effective, enhancing overall operational performance. Accurate calculations in both existing and new processes lead to improved safety, reliability, and sustainability in industrial operations.
Explore Related Services
View All Services →
Energy Audit is defined as “the verification, monitoring and analysis of use of energy including submission of technical report containing recommendations for improving energy efficiency with cost benefit analysis and an action plan to reduce energy consumption”. It builds on the principle "you can't manage what you don't measure". It essentially combines the principles of energy use and statistics.

Energy conservation is the effort made to reduce the consumption of energy by using less of an energy service. This can be achieved either by using energy more efficiently (using less energy for a constant service) or by reducing the amount of service used (for example, by driving less).

Harmonic analysis is a technique used to study and analyze the harmonic components in a periodic waveform or signal. The main use of harmonic analysis in electrical engineering is to examine the existence and properties of harmonics in electrical power systems. Harmonic voltage or current waveform frequencies are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency. However, due to non-linear loads, such as power electronics, variable speed drives, and certain types of lighting, harmonic currents and voltages can be introduced into the system.

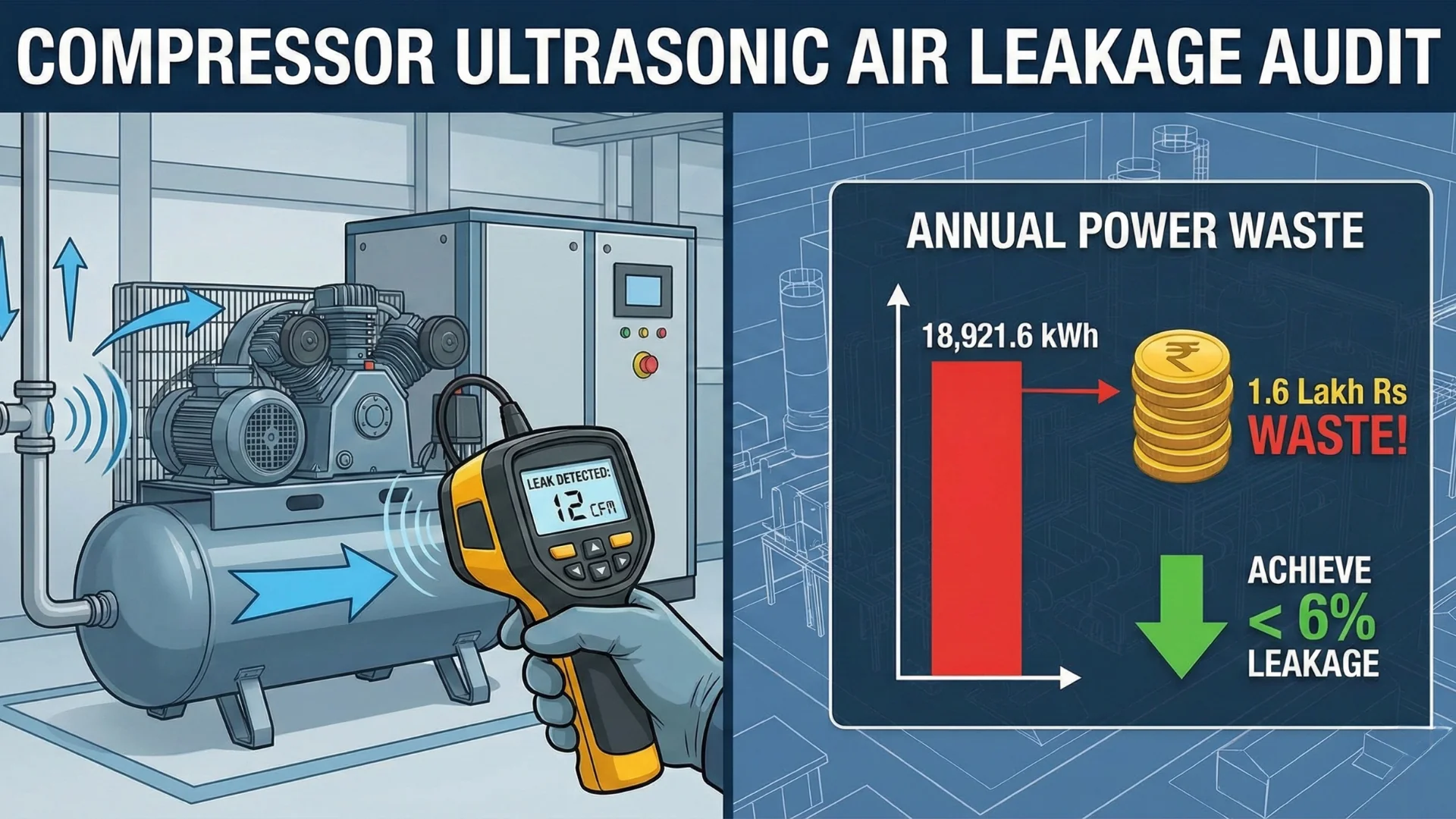
A compressed air audit effectively identifies inefficiencies, reduces energy costs, and improves system performance. Many industrial air compressors operate inefficiently due to leaks, artificial demand, and incorrect air pressure requirements, unnecessarily increasing cost per kWh.